Diagnosing Spasmodic Dysphonia
Spasmodic dysphonia (SD) can be difficult to diagnose because the anatomy of the larynx remains normal. SD has no objective pathology that is evident through x-rays or imaging studies like a CT or MRI scan, nor can a blood test reveal any abnormality. As a result, a process of elimination is usually used to diagnose SD.
Adductor versus Abductor SD
Spasmodic dysphonia is generally categorized into two primary forms, adductor (AdSD) and abductor (AbSD) spasmodic dysphonia.
Adductor spasmodic dysphonia
– 80-90% of people diagnosed with SD will suffer from Adductor SD.
– Spasms usually in the thyroarytenoid muscle force the vocal cords together in adduction. May also affect the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle.
– Spasms occur on voiced speech sounds (Link to AD sentences)
– Patient complains that they struggle to speak
– You can often hear breaks in their voice
Link to AD reference sentences
Abbductor spasmodic dysphonia
– Occurs in approximately 10-20% of those diagnosed with SD
– Occurs when spasms in the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles abduct, or open. As a result, vocal folds stay open for longer than normal.
– Patient often sounds airy or breathy because they expend too much air during speech.
– Voiceless speech sounds impacted (Link to AB sentences)
– Patients feel winded and out of breath when speaking
Link to AB Reference sentences
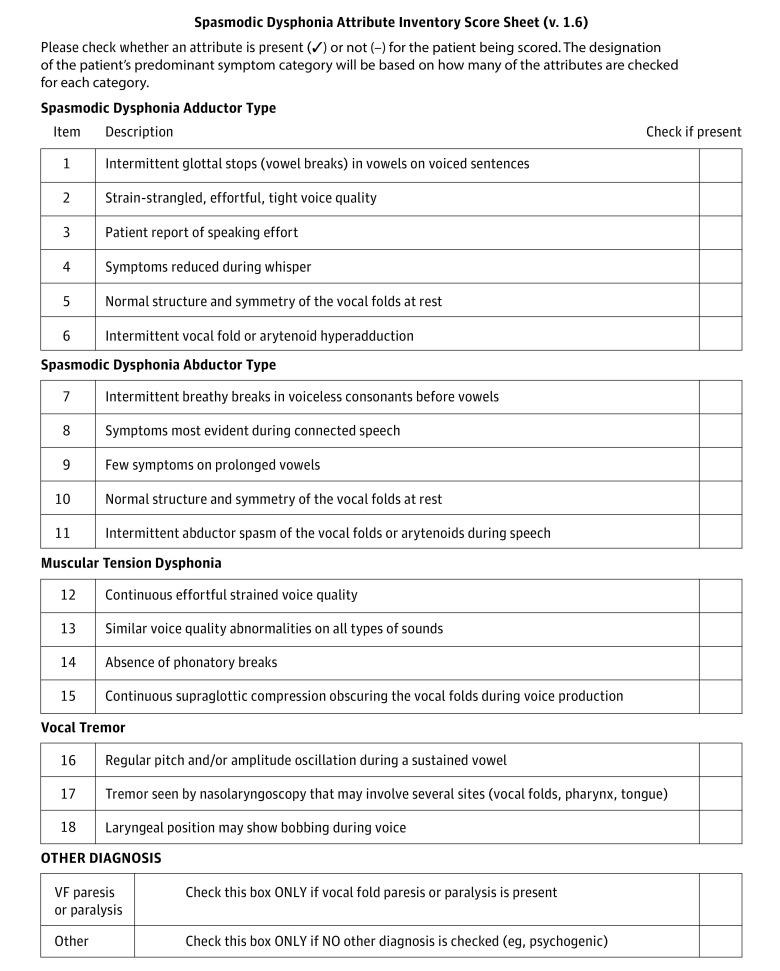
Symptom Checklist
Several other voice disorders may mimic or sound similar to SD. The excessive strain and misuse of muscle tension dysphonia (MTD), the harsh strained voice of certain neurological conditions, the weak voice symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, certain psychogenic voice problems, acid reflux, or voice tremor are often confused with SD. Because of the difficulty in diagnosis, we are sharing an unofficial checklist of symptoms, by disorder. This is not intended to be an all-inclusive list, but provides guidance to shorten the time between symptom onset and diagnosis. The designation of the patient’s predominant symptom category will be based on how many of the attributes are checked for each category.
JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Aug; 144(8): 657–665.


