Botulinum neurotoxin injections to treat symptoms of spasmodic dysphonia
Botulinum neurotoxin (BNT) is a common treatment used to reduce the symptoms of spasmodic dysphonia since the mid-1980s. Botulinum toxin is derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is a nerve “blocker” that binds to the nerves that lead to the muscle and prevents the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that activates muscle contractions. After a short period of time, typically several months, the nerve endings regenerate, the muscle gradually regains strength and muscle contractions or “spasms” return. It is recognized as an effective treatment by the American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery.
In spasmodic dysphonia, laryngeal muscles spasm because too many of the wrong type of signals travel from the brain through the nerves and into the muscles. Botulinum neurotoxin, a biologic product, is injected directly injected into the affected muscles. Botulinum neurotoxin blocks these nerve signals, reducing the number and severity of the spasms.
BNT generally lasts an average of three months but duration of benefit depends on several factors such as severity of the SD, dosage received, unilateral or bilateral injection and the presence or absence of tremor.
It may require several injections to establish the optimal individualized dose, as it can be different for each person. Optimal dosage is a balance of duration of injection side effects/breathiness and duration of clear voice. Some may prefer to have a stronger dosage with a longer period of breathiness after the injection and a longer duration of optimal voice (requiring fewer shots per year), while others may prefer to minimize the side effect duration to opt for shorter lasting, more frequent injections. Two different individuals may also have different results from the same dosage (due to differing anatomy, neurology, severity of SD etc.) so initial dosages must be trialed and tailored to fit the individual’s needs. Individuals may choose to time injections around important speaking events (i.e. presentations, weddings). Unilateral injections may offer a good option for some individuals desiring less side effects.
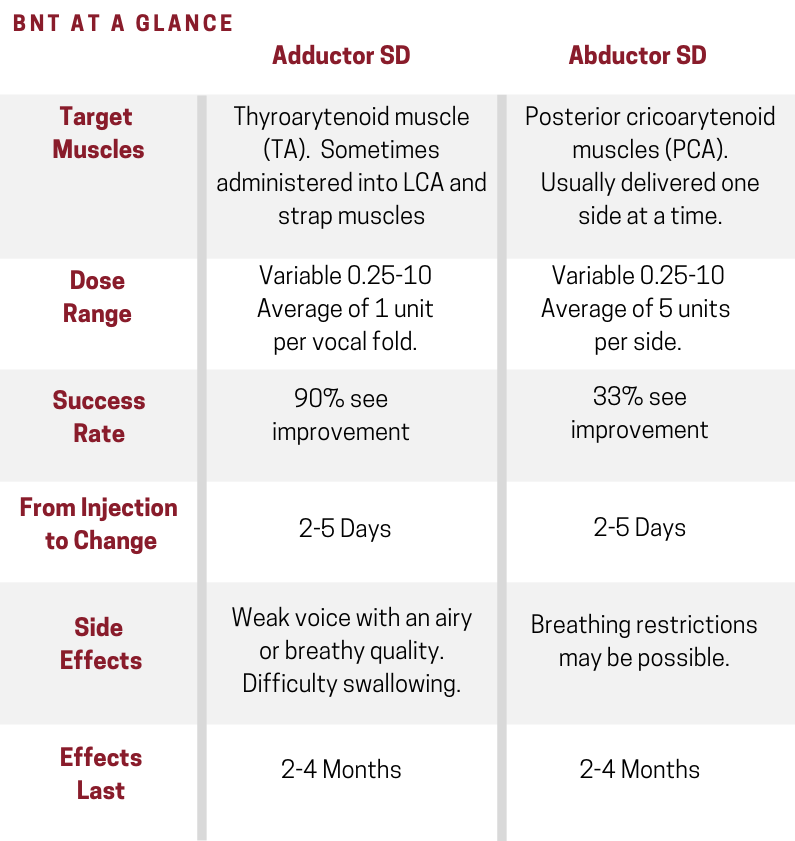
What muscles are injected for SD?
In AdSD the target muscles are often the TA, although some practitioners prefer to dose the LCA as well. These muscles are active in closing the larynx; weakening them prevents the voice breaks associated with AdSD.
People with AbSD typically receive injections in the PCA. Weakening the muscles that open the larynx keeps the vocal cords closer together, thus preventing the breathy voice breaks associated with this subtype.
Persons with tremor may have their laryngeal strap muscles injected for improvement. The strap muscles, located in the neck, support the voice box and are often affected in tremor. In certain circumstances, the other smaller muscles such as the CT or the IA may be injected as well.
What are the methods for injections?
Botulinum toxin needs to be injected with a needle directly into the desired muscle for effect. The higher the dose, the weaker the muscle becomes, but this must be balanced with consideration for possible side-effects. The majority of physicians administer the medicine in an office setting without any special preparation. Physicians may inject the affected muscles on one side (unilateral injections), or both sides (bilateral injections), together at one or separately in two sittings.
The three most common injections are:
EMG (Electromyography needle): This procedure is most commonly done. It involves the needle being placed through the skin, underneath the voice box, and up into the vocal cords. The activity signal is used in this needle to guide the Physician properly into the muscle.
The Point-Touch Technique: Using the anatomic landmarks that are on the voice box, the physician is able to guide the botulinum toxin injections into the correct muscles without an EMG.
The Direct Approach: This is normally done through the mouth (trans-oral). This allows the needle to be placed into the vocal cord, which is done by utilizing a camera that is either inserted in the nose or through the mouth. This direct placement of the botulinum toxin injections does not require the Electro-guided needle.
Unilateral versus bilateral injections?
Normally, there is a wide “therapeutic window” when it comes to botulinum toxin injections. This means that the effective dose does not often cause side effects and bilateral injections may provide a more predictable result. However, when the patient possesses a narrow “therapeutic window” the side effects may be present at the lowest effective dose. In this situation, unilateral injections may be beneficial.
Bilateral Injections: This is the more common technique, which involves administering botulinum toxin injections into both the vocal cords.
Unilateral Injections: This technique involves having one vocal cord injected at a time. After a person has had botulinum toxin injections for a while, the physician can determine if they would be a candidate for this injection. It typically involves alternating injections between the right and left vocal cord. This may be as effective as bilateral injections. This technique is done to try and avoid side effects, such as difficulty swallowing or breathiness.
What is the normal dosage?
A wide variety of doses are used, but most people receive less than five units per muscle. Every peron’s dosage will be different. Sometimes people aren’t even the same from injection to injection. Due to this, dosages are often being adjusted. Communication is very important, as both the patient and the physician need to determine what is the right dosage.
While about 90 percent of AdSD patients are successfully treated with botulinum toxin injections, only one-half to two-thirds with AbSD find botulinum toxin injections treatment helpful. This perhaps occurs because physicians consciously limit the dose delivered to the PCA, as these muscles are also intricately involved in respiration. A large dose delivered to these muscles could cause a patient to experience difficulty with breathing. Many physicians stage the dose from side-to-side or only inject one side in patients with AbSD for this very reason.
Are there any recommendations after an injection?
Your doctor will give you specific information for speaking following your injection. Some recommend speaking normally and some recommend a short period of vocal rest. During the weak period, you may experience that your voice fatigues quickly. Avoid pushing through this period and straining your voice. Rest your voice frequently, especially when your voice feels tired. Avoid speaking in loud environments, shouting, or yelling. Avoid coughing as much as possible.
Are there any side-effects?
An individual may experience some soreness at the spot of injection the day of the injection. This should resolve quickly after the injection. Bruising is uncommon.
Swallowing problems (i.e., coughing with eating and drinking, or food/liquid “slipping down the wrong pipe”) occur in some patients after receiving BoTox, as the vocal folds serve to produce voice but also as a protector of our airway during swallowing. Weakening of the muscles results in less closure of the vocal folds during swallowing with a potential risk of aspiration of thin liquids or foods. Thin liquid (i.e., water, tea, coffee) is the consistency that commonly gives people the most difficulty. If you do experience swallowing problems, they should resolve as your voice strengthens and progresses to the near-normal/normal period. Using a straw may help.
The botulinum neurotoxin usually begins to work for about two days. After this short time, the targeted muscles weaken and the person may experience some changes. In AdSD, people often develop a weak voice with an airy or breathy quality. Some describe a voice that sounds like Mickey or Minnie Mouse. The weak voice generally lasts only for a few days. The stronger voice lasts on the order of three months. In AdSD, if the dose is too high, breathing can be affected. It is important to contact your doctor if you are having any issues.
Following this, the effect of the BNT wears away and the voice returns to baseline status. Most physicians try to minimize the negative effects of weak voice and maximize the good voice. This is done by adjusting the doses. The physician depends on you relaying your experiences so that the doses can be appropriately adjusted. Some people keep a diary to chart their voice between injections. People with AbSD may experience a similar period, but may have less of the ups and downs in the beginning. As injection of the PCA can lead to some restriction of breathing, it is important that you inform the doctor how they felt so that good voice can be balanced with good breathing.
Are these injections safe?
The botulinum toxin injections are safe. It is administered at very low doses and there are minimal side effects. It is used for treating a variety of disorders. People can build up a botulinum toxin immunity when large doses are administered. This is rarely the case in SD, but a blood test can be performed to identify if this is a problem.
What can I do during the breathy period?
You may work with a speech language pathologist to learn resonant and easy voicing strategies. An amplifier may be helpful for some individuals during the weakened stage. To avoid amplifying the side effects, avoid straining and pushing your voice and try to speak with more ease and breath. You may overarticulate sounds at your lips to be heard more clearly and use non-verbal communication when needed (writing, whiteboard, text to speech etc.).
What are the drawbacks of this treatment?
- There are side effects for up to two weeks including breathiness, weak or high pitched voice, mild pain at site of injection and possible difficulty swallowing.
- May be costly for some or not covered by insurance.
- Some may not receive benefits, especially those with AbSD or AdSD with tremor.
- Establishing optimal dosage (balance of optimal effect with minimal side effects) is “trial and error” and can take about doses on average to establish.
- Some may experience a “missed” injection occasionally if the injection does not hit the exact right spot.
- Not a permanent solution -Need for repeated injection every 3-4 months on average.
What if they do not work?
It may take a few tries to find the optimal dose for relief of your symptoms. However some things to be considered if you are not getting a response include:
— Inaccurate delivery/placement of the toxin (missing the spot)
— Inappropriate dosage
— Incorrect diagnosis
— Disease progression
— Co-existence of other neurological disorder or voice condition
— Antibody development
The best outcomes for the botulinum toxin injections involves time and a team effort between the individual and his/her physician. T
Background on BNT and Types of Toxins
Use of botulinum toxin specifically for SD began in 1984, and since then it has been used to treat thousands of people with SD with its efficacy and safety documented in numerous medical publications. Furthermore, the American Academy of Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery has documented its use for SD in a policy statement. Its use by physicians to treat SD is termed “off-label.” Many other medicines are used successfully off-label and the FDA approval does not limit a physician’s use of a medicine. Botulinum toxin exists in a number of forms, but only types A and B are available commercially. Both are administered similarly but have different dosing, onset of action, and length of activity. The majority of people with SD receive botulinum toxin type A.